1. What is a Macromolecule?
A macromolecule isa molecule containt a very large number of atoms. Also a class of large molecules.
2. What is a monomer?
A small molecule that is a subunits of a polymer.
3. What is a ploymer?
It's the largest macromolecule because they are linked together by large numbers of subunits called momomers.
4. List the 4 main types of Macromolecules?
Type Example
Proteins Polypeptide
Lipids Fat
Carbohydrates Polysaccharide
Nucleic Acids DNA, RNA
5. What are the types of reactions that Macromolecules are shown to undergo?
Macromolecules under hydrolysis reactions and and condensation reactions.
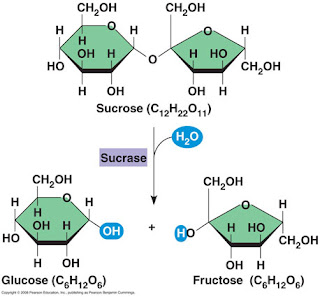
6. Describe how monomers are joined together.
Momomers are joined by dehydration synthesis.A covalent bond is formed between 2 monomers while water is formed by the OH groups.
7. Describe now polymers are broken down.
Polymers are broken down by hydrolysis reactions. A water molecule with the help of a hydrolase enzyme breaks the covalent bond that is holding the monomers together.
8. What's the specific name for the bond between simple sugar monomers?
A covalent bond.
9. Which kind of enzyme joins monomers together?
The hydrolase enzyme is what joins monomers together.
10. Describe how you had to arrange the sugar monomers in order to build a polysaccharide.
First I added a sugar molecule to another sugar molecule to form a glycosidic linkage. Next I add another sugar molecule to the other two sugar molecules. The oxygen molecules hold the sugar molecules together when i rotated it. I rotated it to separate the hydrogen molecules so that once the oxygen molecules where connected H2O was formed. Once all 4 sugar molecules where linked the bonds where held together and I created a 4-molecule polysaccharide.
11. Which building blocks of macromolecules are not used in building carbohydrates?
Amino acids, fatty acids, and nucleotide are not used to build a carbohydrate.
12. Why is sugar stored as glycogen in the human body?
Glycogen is stored in the human body. Glycogen is stored in the muscles and once its stored in the muscles it can't be released. Also it's stored in the liver because the liver helps regulate the amount of sugar goes into the blood stream. This balances out our blood sugar levels.
13. Why are plant foods essential in animal life?
Glucose is the fuel in all living things. Plants produce sugar during there living process. Our bodies have a hard time producing glucose and by eating vegetables and fruits we take in all of that glucose to store.
14. Describe how starch is digested by animals.
The starch first starts to digest first in the mouth with salivary amylase. It goes into the small intestines digesting in pancreatic amylase. Glucoamylase breaks the short chains of alpha-dextrin(glucoses) into individual glucose molecules that are then absorbed.
15. What is fiber and why is it important in your diet?
Fiber is filament formed from vegetable tissue, mineral substance, or textile. Fiber is important in our diet because it reduces the risk of cancers, diabetes, digestive disorders and heart disease.
16. What causes you to pass gas(fart) according to the article?
Indigestable carbohydrates produce gas.
17.disadvantages to a low-carb diet.
The disadvantages are that in the first few months there is a great weight loss but in the 12 months both energy and low-carb diets have the same results. Also you don't get enough carbs.
18. Sugars and cavities formation
Acid-producer+Carbohydrates+teeth= Cavities
When you eating sugars it produces acids that cause cavities.